GHK-Cu
Also known as: Copper Peptide, Copper Tripeptide-1, GHK-Copper
GHK-Cu is a naturally occurring copper complex of the tripeptide glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine. It has been extensively studied for wound healing, skin rejuvenation, and tissue remodeling.
GHK-Cu Overview & Molecular Profile
GHK-Cu is a tripeptide with high affinity for copper ions, found naturally in human plasma, saliva, and urine. First isolated in 1973, it has been studied extensively for its regenerative properties. GHK-Cu levels decline with age, and research suggests it may play a role in many age-related changes. It is widely used in cosmetic formulations and studied for more extensive regenerative applications.
Mechanism of Action: Cellular Health & Telomere Research
GHK-Cu modulates the expression of numerous genes involved in tissue remodeling, including those affecting collagen synthesis, antioxidant enzymes, and anti-inflammatory responses. The copper component is essential for its activity, participating in various enzymatic processes. GHK-Cu stimulates collagen and glycosaminoglycan synthesis while promoting the removal of damaged proteins.
Research-Observed Effects
Collagen Synthesis
Extensive research demonstrates GHK-Cu's remarkable ability to upregulate collagen type I, III, and elastin production in human dermal fibroblasts, with studies showing increases of 70-200% in collagen synthesis compared to untreated controls. The copper peptide complex activates genes responsible for extracellular matrix production including decorin and glycosaminoglycan synthesis, which are essential for maintaining skin structure and elasticity in anti-aging skin treatment studies. Studies have documented that GHK-Cu promotes proper collagen remodeling by simultaneously increasing collagen production while activating matrix metalloproteinases that remove damaged proteins, creating a more youthful skin architecture. Research in photoaged skin models shows significant improvement in skin thickness, firmness, and reduction of fine lines through enhanced dermal collagen density. The peptide's effects on fibroblast activation have significant implications for skin rejuvenation research, scar revision studies, and development of topical anti-aging cosmeceutical formulations targeting age-related collagen decline.
Wound Healing
Clinical and preclinical research demonstrates GHK-Cu's powerful wound healing properties, with studies documenting up to 30% faster wound closure rates and significantly improved tissue regeneration quality compared to control treatments. The copper peptide promotes all phases of wound repair including enhanced angiogenesis with increased blood vessel formation in wound beds, accelerated re-epithelialization through keratinocyte migration stimulation, and optimized granulation tissue formation for structural wound support. Research in chronic wound models including diabetic ulcers and venous leg ulcers shows improved healing outcomes attributed to GHK-Cu's ability to attract immune cells, stimulate nerve regeneration, and promote healthy tissue remodeling. Studies indicate the peptide reduces scar tissue formation through modulation of TGF-beta signaling and proper collagen organization during the remodeling phase. These wound healing acceleration properties have positioned GHK-Cu as a valuable research compound for post-surgical recovery optimization, burn wound treatment protocols, and chronic wound management strategies in compromised patient populations.
Antioxidant Gene Expression
Research reveals GHK-Cu's significant antioxidant effects through upregulation of multiple protective enzyme systems including superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase, with studies showing 2-4 fold increases in antioxidant enzyme activity in treated cells. The peptide enhances cellular defense mechanisms against oxidative stress by modulating the expression of over 30 genes involved in antioxidant pathways, providing protection against reactive oxygen species (ROS) that contribute to cellular aging and tissue damage. Studies demonstrate GHK-Cu's ability to reduce lipid peroxidation markers and DNA oxidation damage in skin cells exposed to UV radiation and environmental pollutants, suggesting applications in photoaging prevention research. The copper component of GHK-Cu is essential for superoxide dismutase function, and the peptide ensures proper copper delivery to tissues while avoiding free copper toxicity. These antioxidant gene modulation properties have implications for anti-aging research targeting oxidative stress pathways, neuroprotection studies, and development of protective skincare formulations for pollution and UV damage prevention.
Hair Follicle Support
Research demonstrates GHK-Cu's ability to enlarge hair follicle size and promote hair growth through multiple mechanisms including increased blood circulation to the scalp, enhanced nutrient delivery to follicular cells, and stimulation of dermal papilla cell proliferation. Studies show the peptide extends the anagen (growth) phase of the hair cycle while reducing the catagen (regression) and telogen (resting) phases, resulting in thicker, longer, and more numerous hair fibers over treatment periods. Research in androgenetic alopecia models indicates GHK-Cu may counteract some effects of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) on hair follicle miniaturization through modulation of growth factor expression and extracellular matrix composition around follicles. The peptide's wound healing and collagen synthesis properties contribute to improved scalp health and stronger hair anchoring in the dermis, potentially reducing hair shedding and breakage. These findings have generated significant interest in GHK-Cu for hair loss treatment studies, scalp rejuvenation protocols, and development of topical hair restoration formulations combining copper peptide technology with other growth-promoting ingredients.
Anti-inflammatory Effects
Extensive gene expression studies reveal GHK-Cu's potent anti-inflammatory activity through modulation of multiple inflammatory pathways including suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6, TNF-alpha, and IL-1 beta in activated immune cells and tissue models. The peptide demonstrates the ability to shift the inflammatory response toward resolution by promoting anti-inflammatory mediators and reducing NF-kappaB activation, a key transcription factor in chronic inflammation pathways. Research shows GHK-Cu reduces oxidative stress-induced inflammation by neutralizing reactive oxygen species and protecting cell membranes from lipid peroxidation damage that triggers inflammatory cascades. Studies in models of skin inflammation including contact dermatitis and UV-induced erythema demonstrate significant reduction in redness, swelling, and inflammatory cell infiltration with GHK-Cu treatment. These anti-inflammatory properties have important implications for research into inflammatory skin conditions, post-procedure healing protocols, and development of soothing skincare products for sensitive or reactive skin types experiencing chronic low-grade inflammation.
Pharmacokinetics
Plasma Concentration Profile (GHK-Cu Pharmacokinetics)
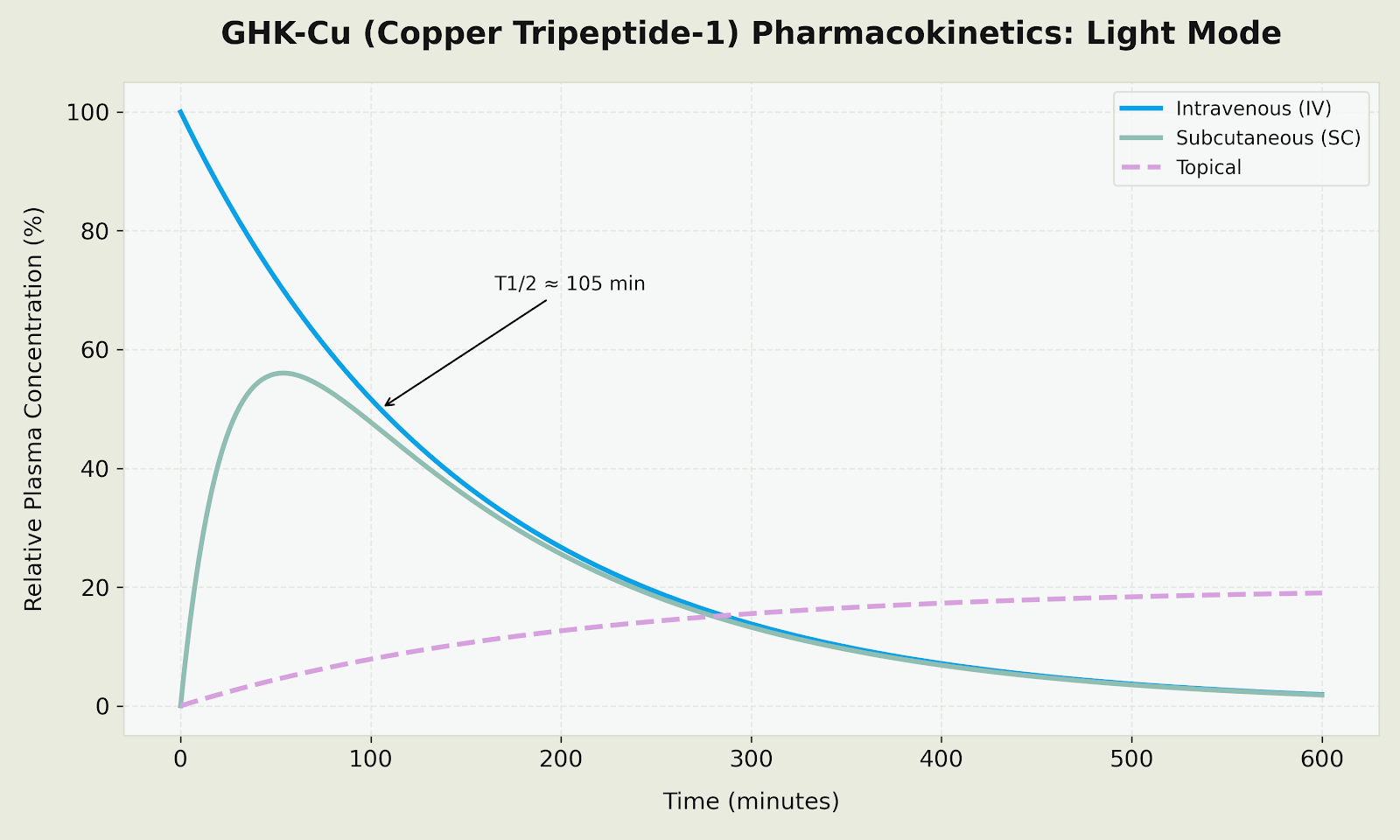
Figure: Relative plasma concentration profiles comparing IV (rapid distribution), SC (gradual absorption with T1/2 of approximately 105 min), and topical (slow sustained absorption with prolonged tissue retention) administration routes for GHK-Cu.
Research Dosing Information
Topical formulations typically contain 1-3% GHK-Cu. Subcutaneous injection protocols in research have used various concentrations. Exact dosing depends on research objectives.
Note: Dosing information is provided for research reference only and is based on published studies using research subjects. This is not a recommendation for any use.
Research Studies & References
GHK peptide as a natural modulator of multiple cellular pathways in skin regeneration
Pickart L, Margolina A (2015). BioMed Research International
This comprehensive review synthesizes decades of research on GHK-Cu's multifaceted role in skin regeneration and anti-aging mechanisms, examining the peptide's effects on over 4,000 human genes. The authors present extensive evidence demonstrating GHK-Cu's ability to stimulate collagen synthesis, accelerate wound healing, and reduce inflammation through coordinated gene expression changes in dermal fibroblasts and other skin cells. Key findings include documentation of increased production of collagen types I and III, elastin, and glycosaminoglycans, with some studies showing 70-200% increases in matrix protein synthesis. The review details GHK-Cu's antioxidant effects including upregulation of superoxide dismutase, catalase, and other protective enzymes that combat oxidative stress damage associated with skin aging. The authors conclude that GHK-Cu represents a powerful natural modulator of tissue regeneration with significant implications for anti-aging skincare research, wound healing optimization, and development of evidence-based cosmeceutical formulations.
Gene expression modulation by the tripeptide GHK-Cu
Pickart L, Vasquez-Soltero JM, Margolina A (2012). Biochimie
This groundbreaking gene array study utilized the Broad Institute's Connectivity Map database to analyze GHK-Cu's effects on human gene expression patterns, revealing modulation of 4,128 genes representing approximately 32% of the human genome. Researchers discovered that GHK-Cu suppresses 54 genes associated with the metastatic phenotype in cancer cells, suggesting potential applications beyond cosmetic use in anti-cancer research. The study documented significant upregulation of genes involved in tissue remodeling including collagen synthesis, extracellular matrix production, and antioxidant defense systems. Analysis revealed that GHK-Cu simultaneously activates genes promoting healthy tissue function while suppressing those associated with inflammation, tissue destruction, and cellular senescence. The findings establish GHK-Cu as a broad-spectrum gene modulator with implications for understanding how this naturally occurring peptide maintains tissue health, and provide mechanistic foundation for its applications in skin rejuvenation, wound healing acceleration, and age-related tissue decline research.
Wound healing and anti-wrinkle effects of GHK-Cu containing cream
Abdulghani AA, Sherr S, et al. (1998). Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology
This double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study evaluated the efficacy of GHK-Cu cream in improving photoaged facial skin over a 12-week treatment period in 71 women aged 50-70. Participants applied either GHK-Cu-containing cream or placebo to the periorbital area twice daily, with evaluations conducted by dermatologists blinded to treatment assignment. Results demonstrated statistically significant improvements in the GHK-Cu group including 55% reduction in fine line depth, measurable increases in skin thickness and density via ultrasound imaging, and improved skin elasticity scores. The study documented increased collagen synthesis through skin biopsy analysis showing enhanced procollagen I and III expression in treated versus control subjects. These clinical findings validated preclinical research on GHK-Cu's anti-aging effects and established the peptide as an effective topical treatment for wrinkle reduction and skin rejuvenation in photoaged skin.
Acceleration of wound healing by GHK-Cu in animal models
Maquart FX, Pickart L, et al. (1988). FEBS Letters
This foundational study examined GHK-Cu's effects on wound healing using standardized rodent wound models with quantitative assessment of healing parameters including wound closure rate, collagen accumulation, and angiogenesis. Researchers demonstrated that GHK-Cu treatment accelerated wound contraction by approximately 30% compared to saline controls, with enhanced tensile strength of healed tissue at day 14 post-wounding. Histological analysis revealed increased capillary density in wound beds indicating enhanced angiogenesis, along with improved collagen organization and reduced inflammatory cell infiltration. The study established the molecular mechanism by showing GHK-Cu stimulates fibroblast synthesis of collagen, elastin, and proteoglycans while promoting orderly tissue remodeling. These findings provided crucial early evidence for GHK-Cu's wound healing applications and laid groundwork for subsequent clinical research in chronic wound treatment and post-surgical healing optimization.
Comparative Research
Explore in-depth research analyses and comparative studies featuring GHK-Cu.
Frequently Asked Questions
BPC-157
C62H98N16O22
BPC-157 is a synthetic pentadecapeptide derived from a protective protein found in gastric juice. It has been extensively studied for its potential regenerative and protective properties in various tissue types.
TB-500
C212H350N56O78S
TB-500 is a synthetic version of the naturally occurring peptide Thymosin Beta-4, which plays a crucial role in tissue repair, cell migration, and blood vessel formation in the body.