TB-500
Also known as: Thymosin Beta-4, Tβ4, Thymosin B4
TB-500 is a synthetic version of the naturally occurring peptide Thymosin Beta-4, which plays a crucial role in tissue repair, cell migration, and blood vessel formation in the body.
TB-500 Overview & Molecular Profile
TB-500, also known as Thymosin Beta-4, is a 43 amino acid peptide that is naturally present in nearly all human and animal cells. It is particularly concentrated in wound fluid, blood platelets, and other tissues involved in healing. The synthetic version has been extensively studied for its role in promoting tissue regeneration, wound healing, and cellular repair mechanisms. TB-500 is unique in its ability to travel long distances through tissues due to its molecular structure.
Mechanism of Action: Gene Activation & Angiogenesis
TB-500 works primarily by upregulating actin, a cell-building protein that plays a crucial role in cell migration, division, and proliferation. The peptide promotes cell migration by forming a complex with actin, allowing cells to move to areas requiring repair. It also promotes angiogenesis and reduces inflammation. TB-500 has been shown to interact with HIF-1 alpha and VEGF pathways, promoting new blood vessel formation in damaged tissues.
Research-Observed Effects
Enhanced Cell Migration
Research demonstrates TB-500's critical role in promoting cell migration to injury sites through direct interaction with G-actin, facilitating actin polymerization and cytoskeletal reorganization essential for cell motility. The peptide has been shown to promote migration of endothelial cells, keratinocytes, and various stem cell populations toward damaged tissue areas. Studies document TB-500's ability to increase cell migration speed and directional persistence through modulation of integrin-linked kinase (ILK) signaling pathways. This enhanced cellular mobility is fundamental to wound healing processes, tissue regeneration after injury, and vascular repair mechanisms. Research indicates TB-500's unique low molecular weight allows it to travel through tissues more effectively than many other healing factors, potentially affecting distant injury sites.
Wound Healing Promotion
Extensive studies demonstrate TB-500's multi-faceted approach to wound healing including promotion of angiogenesis for improved blood supply to healing tissues, enhanced keratinocyte differentiation for skin regeneration, and acceleration of collagen matrix deposition for structural tissue repair. Research in dermal wound models shows significantly faster wound closure times, improved wound contraction, and superior cosmetic outcomes with reduced scarring. The peptide promotes formation of new blood vessels through upregulation of VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) and interaction with HIF-1 alpha pathways. Studies in chronic wound models including diabetic ulcers and pressure sores demonstrate enhanced healing even in compromised tissue environments. TB-500 has been investigated for burn wound treatment applications, surgical incision healing, and traumatic wound recovery.
Cardiac Tissue Repair
Groundbreaking research published in Nature and other high-impact journals demonstrates TB-500's significant potential for cardiac tissue regeneration following myocardial infarction (heart attack). Studies show the peptide promotes cardiac muscle cell survival, reduces scar formation in damaged heart tissue, and may stimulate cardiomyocyte regeneration from progenitor cells. Research indicates TB-500 activates integrin-linked kinase in cardiac cells, promoting survival signaling and reducing apoptosis after ischemic injury. Animal studies have documented improved cardiac function, reduced infarct size, and enhanced left ventricular ejection fraction following treatment. The peptide has been investigated for applications in coronary artery disease research, heart failure mechanisms, and post-heart attack recovery optimization strategies.
Hair Follicle Stimulation
Preliminary research suggests TB-500 may promote hair follicle stem cell activation, migration, and differentiation through its effects on cell motility and tissue regeneration pathways. Studies indicate the peptide may enhance blood supply to hair follicles through angiogenic mechanisms, potentially improving nutrient delivery to growing hair. Research in animal models has documented increased hair density, accelerated hair regrowth after shaving, and improved follicle health in treated subjects. The peptide's effects on keratinocyte migration and epithelial cell function may contribute to hair shaft formation and quality. These findings have generated interest in TB-500 for androgenetic alopecia (male and female pattern baldness) research, alopecia areata mechanisms, and chemotherapy-induced hair loss recovery studies.
Anti-inflammatory Properties
Research demonstrates TB-500's significant anti-inflammatory effects through reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokine expression including IL-1 beta, TNF-alpha, and various chemokines involved in inflammatory cell recruitment. The peptide has been shown to reduce oxidative stress markers and reactive oxygen species production in damaged tissues, creating a more favorable environment for regeneration. Studies indicate TB-500 may modulate macrophage polarization from pro-inflammatory M1 to pro-regenerative M2 phenotypes, enhancing the transition from inflammatory to healing phases. Research in models of inflammatory conditions including colitis, arthritis, and dermatitis shows reduced tissue damage and accelerated resolution of inflammation. These anti-inflammatory properties appear synergistic with tissue repair mechanisms, contributing to faster overall recovery in injury models.
Pharmacokinetics
Plasma Concentration Profile (TB-500 Pharmacokinetics)
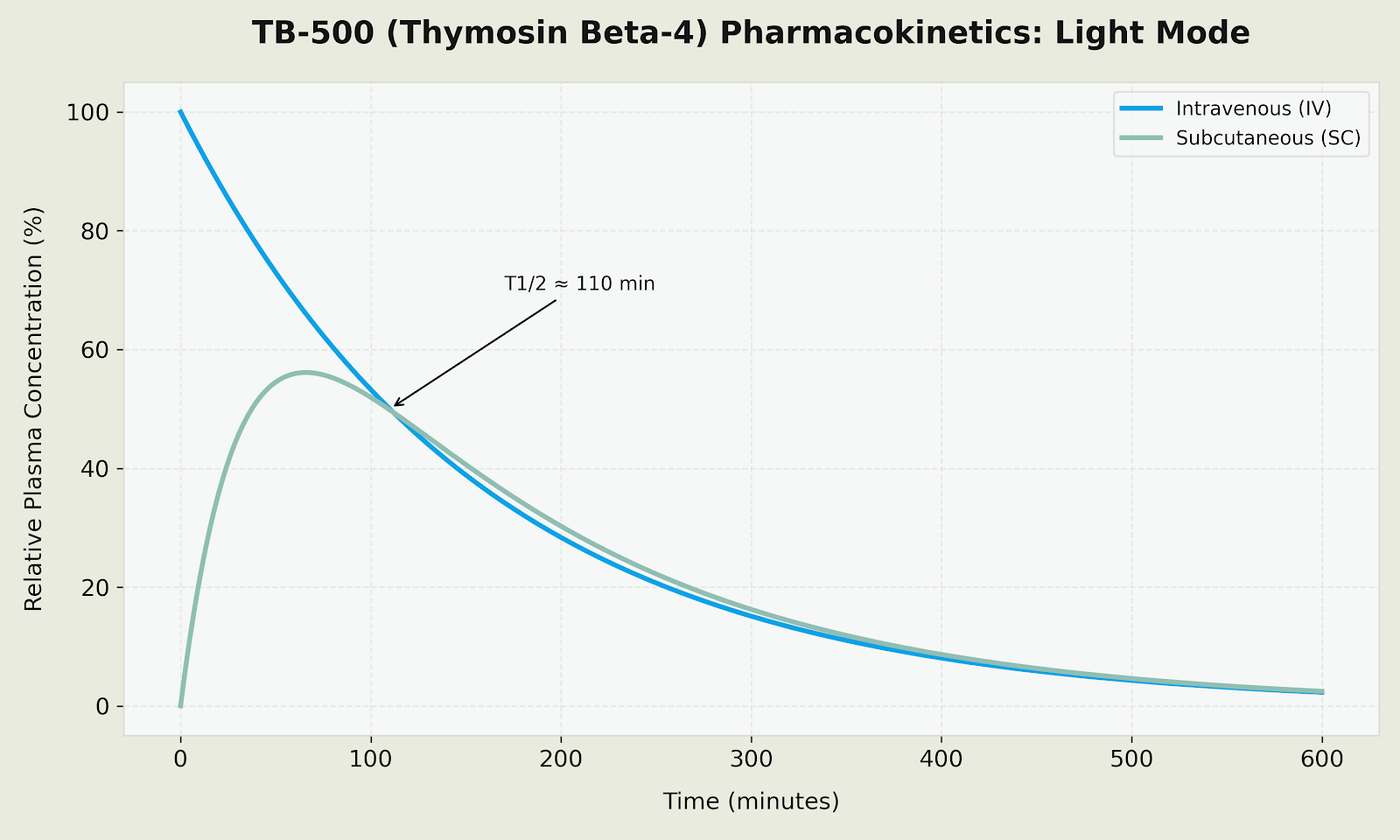
Figure: Relative plasma concentration profiles comparing IV (rapid distribution) and SC (gradual absorption with T1/2 of approximately 110 min) administration routes for TB-500.
Research Dosing Information
Research protocols have varied significantly depending on the study design and model organism. Animal studies have used dosages ranging from 0.1 mg to 10 mg administered at various intervals. Routes of administration in research include subcutaneous, intramuscular, and intravenous injection. Specific protocols should be referenced from original research publications.
Note: Dosing information is provided for research reference only and is based on published studies using research subjects. This is not a recommendation for any use.
Research Studies & References
Thymosin beta4 promotes dermal healing
Malinda KM, Sidhu GS, et al. (1999). Journal of Investigative Dermatology
This seminal study established TB-500's role in dermal wound healing through a series of in vitro and in vivo experiments examining keratinocyte and endothelial cell behavior. Researchers demonstrated that Thymosin Beta-4 significantly accelerates wound closure in animal models while simultaneously promoting keratinocyte migration and endothelial cell tubule formation. The study revealed that TB-500 treatment increased cell migration rates by 42% in keratinocyte scratch assays and enhanced angiogenesis in wound beds. Histological analysis showed improved collagen organization and reduced scar tissue formation in treated wounds. These findings established the foundation for subsequent research into TB-500's therapeutic potential for chronic wounds, burn injuries, and post-surgical healing optimization.
Thymosin beta4 activates integrin-linked kinase and promotes cardiac cell migration
Bock-Marquette I, Saxena A, et al. (2004). Nature
This landmark Nature publication transformed understanding of TB-500's cardioprotective mechanisms by identifying integrin-linked kinase (ILK) as a key mediator of its cardiac effects. The study demonstrated that TB-500 administration following experimental myocardial infarction significantly reduced infarct size and improved cardiac function in mouse models. Researchers showed that the peptide promotes cardiac progenitor cell migration to damaged areas while simultaneously protecting existing cardiomyocytes from apoptosis through Akt/protein kinase B signaling activation. The study documented improved left ventricular function, reduced fibrosis, and enhanced neovascularization in treated animals. These groundbreaking findings positioned TB-500 as a promising candidate for cardiac regeneration research and opened new avenues for investigating heart attack recovery and heart failure treatment mechanisms.
Thymosin beta 4 promotes angiogenesis, wound healing, and hair follicle development
Philp D, Nguyen M, et al. (2007). Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences
This comprehensive study examined TB-500's multi-tissue effects on angiogenesis, wound healing, and hair follicle biology across multiple experimental models. Researchers documented enhanced blood vessel formation through VEGF pathway activation, accelerated wound closure in both acute and chronic wound models, and stimulation of hair follicle stem cell migration and differentiation. The study demonstrated that TB-500 promotes endothelial cell differentiation and tubule formation in vitro while enhancing hair shaft elongation and follicle cycling in vivo. Analysis revealed the peptide's effects on stem cell mobilization and tissue-specific progenitor cell activation. These findings established TB-500 as a multifunctional regenerative peptide with applications spanning dermatology, cardiovascular research, and hair loss treatment investigations.
Comparative Research
Explore in-depth research analyses and comparative studies featuring TB-500.
Frequently Asked Questions
BPC-157
C62H98N16O22
BPC-157 is a synthetic pentadecapeptide derived from a protective protein found in gastric juice. It has been extensively studied for its potential regenerative and protective properties in various tissue types.
GHK-Cu
C14H23CuN6O4
GHK-Cu is a naturally occurring copper complex of the tripeptide glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine. It has been extensively studied for wound healing, skin rejuvenation, and tissue remodeling.